Now Discover Kidney Stone Risks and Safety Factors
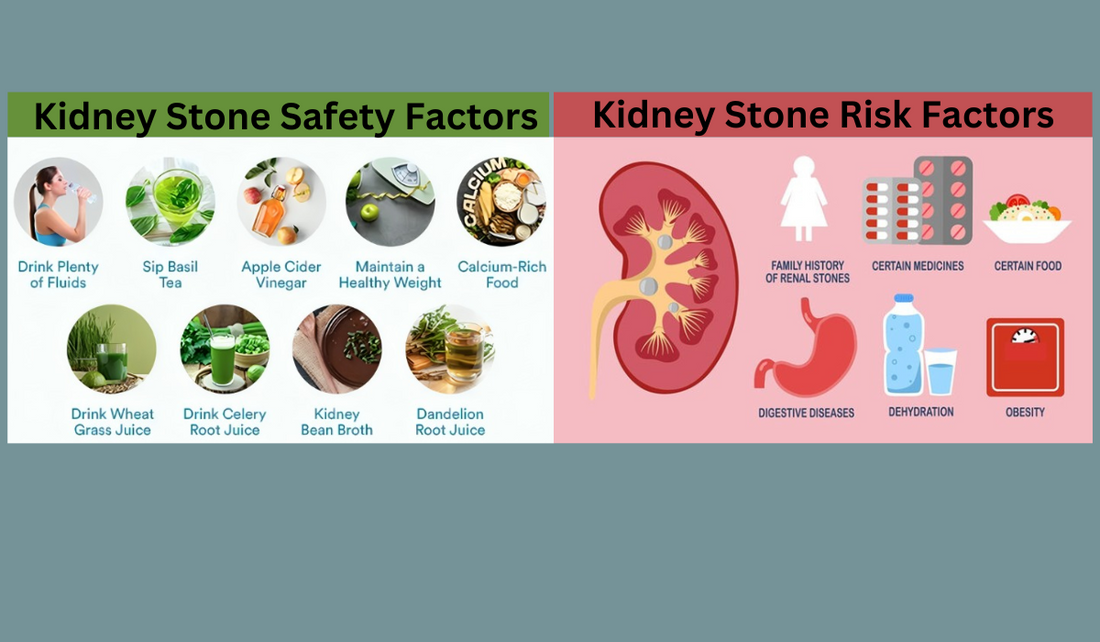
Understanding Kidney Stone Risk Factors
Kidney stones can be excruciatingly painful, and understanding the risk factors associated with their formation is crucial for prevention and management. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the various kidney stone risk factors and provide valuable insights into mitigating their occurrence.

Dietary Factors
Diet plays a pivotal role in the development of kidney stones. High intake of sodium and animal proteins can increase the risk significantly. Foods rich in oxalate, such as spinach, nuts, and chocolate, can also contribute to stone formation. Conversely, a diet abundant in calcium can help bind oxalates in the intestines, reducing their absorption and lowering the risk of stone formation.
Hydration Status
Adequate hydration is essential for preventing kidney stones. Insufficient fluid intake can lead to concentrated urine, which facilitates the crystallization of minerals and salts, culminating in stone formation. Consuming at least 8 to 10 glasses of water per day helps maintain optimal urine volume and dilution, thereby reducing the risk of stone formation.
Lifestyle Factors
Several lifestyle habits can influence kidney stone formation. Obesity is associated with an increased risk due to metabolic changes and higher urinary excretion of calcium and uric acid. Sedentary lifestyle contributes to metabolic imbalances and reduced urinary output, predisposing individuals to stone formation. Regular physical activity promotes overall health and helps maintain optimal weight, reducing the risk of kidney stones.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions predispose individuals to kidney stone formation. Hypercalciuria, characterized by excessive urinary calcium excretion, increases the likelihood of stone formation. Hyperparathyroidism leads to elevated levels of calcium in the blood, which can contribute to stone formation. Other conditions such as gout, cystinuria, and renal tubular acidosis also heighten the risk of kidney stones.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics play a role in determining an individual's susceptibility to kidney stones. Family history of stone formation increases the likelihood of developing stones. Certain genetic disorders, such as cystinuria and primary hyperoxaluria, significantly elevate the risk. Understanding one's genetic predisposition can aid in implementing targeted preventive measures.
Medications and Supplements
Some medications and supplements can influence kidney stone formation. Diuretics increase urinary excretion of calcium and other minerals, potentially leading to stone formation. High doses of vitamin D and calcium supplements may also elevate the risk. It is crucial to consult healthcare professionals before initiating any new medications or supplements, especially for individuals prone to kidney stones.
Understanding Kidney Stone Safety Factors
Understanding the safety factors related to kidney stones is paramount for preventing their formation and safeguarding one's health. In this insightful article, we explore the various kidney stone safety factors and provide valuable insights into mitigating the risks associated with them.

Hydration and Fluid Intake
Maintaining adequate hydration is a cornerstone of kidney stone prevention. Ample fluid intake helps dilute urine, reducing the concentration of minerals and salts that can crystallize and form stones. Water is the best choice for hydration, but other fluids such as herbal teas and fruit juices can also contribute to overall fluid intake. Aim to consume at least 8 to 10 glasses of water per day, and increase intake during hot weather or physical activity to ensure optimal hydration levels.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary choices play a significant role in kidney stone formation. Certain foods are known to increase the risk of stone development, while others can help prevent their occurrence. Limiting intake of sodium, animal proteins, and foods high in oxalates such as spinach, nuts, and chocolate can reduce the risk of stone formation. Conversely, incorporating foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products, can help bind oxalates in the intestines, preventing their absorption and reducing the risk of stone formation.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for kidney stone prevention. Obesity is a known risk factor for stone formation, as it can lead to metabolic imbalances and increased urinary excretion of calcium and uric acid. Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of kidney stones and promoting overall health.
Medication Review
Reviewing medications with a healthcare professional is crucial for individuals at risk of kidney stones. Some medications can increase the risk of stone formation by altering urinary chemistry or promoting the crystallization of minerals. Diuretics, high doses of vitamin D, and calcium supplements are among the medications that may warrant scrutiny in individuals prone to kidney stones. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help identify and mitigate these risks.
Genetic Considerations
Genetic factors can also influence an individual's susceptibility to kidney stones. A family history of stone formation may indicate a genetic predisposition to the condition. Certain genetic disorders, such as cystinuria and primary hyperoxaluria, significantly increase the risk of stone formation. Understanding one's genetic predisposition can inform personalized preventive measures and guide healthcare decisions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, kidney stone formation is influenced by a myriad of factors ranging from dietary choices to genetic predisposition. By understanding and addressing these risk factors, individuals can significantly reduce their likelihood of developing kidney stones. Embracing a balanced diet, maintaining adequate hydration, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking appropriate medical guidance are paramount in mitigating this painful condition.

